<br>
Tag: Hard Drive
False Drive Offline status on some Q-series models
Description Some drives may show an “offline” status on the hardware tab in ExacqVision Client when Server Version 23.03.1.0 is installed on Q-series models, though data can be read from and written to the drive.Note: This issue manifests itself cosmetically by appearing as if the drive is offline but has no bearing on functionality for… Continue reading False Drive Offline status on some Q-series models
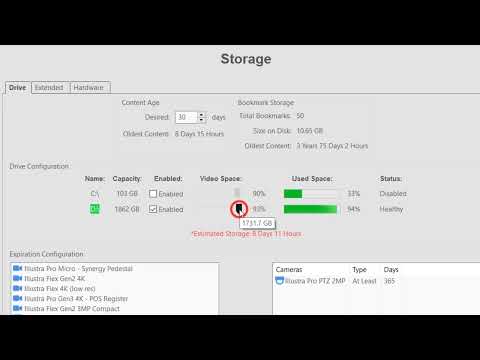
Storage
This video will introduce you to the controls available on the Storage page, which allow you to monitor the health and control which drives are written to. Gain an informed understanding of the Expiration Configuration settings and the retained amount of data stored on your system. Use the Extended tab to optionally connect to a… Continue reading Storage
Replacing the First Storage Drive using GParted on a Non-RAID exacqVision Ubuntu Linux Server having an 8 GB or smaller ROOT partition
Description •This procedure applies to replacing the first non-RAID storage drive (mechanical SATA hard disk drive) on an Ubuntu Linux-based exacqVision server. If the operating system ROOT partition is 8GB or smaller, the replacement primary storage drive will need to have the “Linux swap”, “export”, and first “storage” partitions created on it.•These instructions assume that… Continue reading Replacing the First Storage Drive using GParted on a Non-RAID exacqVision Ubuntu Linux Server having an 8 GB or smaller ROOT partition
Replacing the First Storage Drive using GParted on a Non-RAID exacqVision Ubuntu Linux Server having a 20 GB or larger ROOT partition
Description •This procedure applies to replacing the first non-RAID storage drive (mechanical SATA hard disk drive) on an Ubuntu Linux-based exacqVision server. If the operating system ROOT partition is 20GB or larger, the replacement storage drive will only need to have the first “storage” partition created on it.•These instructions assume that the Linux operating system… Continue reading Replacing the First Storage Drive using GParted on a Non-RAID exacqVision Ubuntu Linux Server having a 20 GB or larger ROOT partition
Scansource Hardware Modifications
Scansource received approval and instructions from the Exacq Engineering team to modify hardware by adding hard drives to existing systems. Since our Tech Support team may need to be aware of the changes, a Sharepoint page with all of the instructions and a spreadsheet with each system that has been modified can be accessed HERE.
2021-02 – Hard Drive Issues Training
Hard Drive Issues Troubleshooting
Hard Drive Self-Test Broken On Older Linux Systems with 9.2
Symptom: When clicking the ‘Self-Test’ button for hard drives, nothing happens. <br> Problem: Introduced in exacqVision Server 9.2.1, a code change broke the self-test functionality for older Linux systems that do not have Smartctl installed. Smartctl is not listed in the ‘Version Information’ panel on the ‘System Information’ page of the client. <br> Solution: Option… Continue reading Hard Drive Self-Test Broken On Older Linux Systems with 9.2
Server May Indicate False HD Temperature Alarms on Systems with LSI RAID
Symptom Client displays temperature alarms on hard drives. These may indicate temperatures near 1° C, or between ~20000-30000° C. <br> Problem This behavior was seen from the following Western Digital HD models when connected to LSI storage controllers. WD4002FYYZWD8002FRYZWD8003FRYZWD6002FRYZWD80PUZXWD101KRYZWD121KRYZ <br> Solution Update the ExacqVision Server version to 9.3.9 or higher, also back-patched into 9.2 RC. <br>
Hard Drive Power on exacqVision EL-SR and EL-IP Systems
EL-SR and EL-ip exacqVision systems were manufactured with hard-drive caddies that contain a power switch starting in October 2011. If it appears that the hard drive in an exacqVision EL-SR or EL-ip system is not functioning even though the system is powered up, look on the front of the system and determine whether a hard… Continue reading Hard Drive Power on exacqVision EL-SR and EL-IP Systems