Description
•This procedure applies to replacing the first non-RAID storage drive (mechanical SATA hard disk drive) on an Ubuntu Linux-based exacqVision server. If the operating system ROOT partition is 8GB or smaller, the replacement primary storage drive will need to have the “Linux swap”, “export”, and first “storage” partitions created on it.
•These instructions assume that the Linux operating system is installed to an on-board solid-state drive (SSD) and can be successfully logged into with an administrator account.
•This procedure is not intended for simply adding a new storage drive to a fully functional system.
Product
exacqVision Ubuntu Linux non-RAID Servers
Solution:
A. Verifying the size of the Root partition is 8 GB or smaller
The root partition size will need to be verified before completing the replacement task properly. Open Terminal and specify the command: df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
udev 1.7G 0 1.7G 0% /dev
tmpfs 339M 4.1M 335M 2% /run
/dev/sda3 55G 9.9G 43G 19% /
tmpfs 1.7G 0 1.7G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock
tmpfs 1.7G 0 1.7G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda2 17G 1.6G 15G 10% /home
/dev/sda4 28G 421M 26G 2% /mnt/export
/dev/sda1 12G 3.1G 8.2G 27% /boot/efi
tmpfs 339M 20K 339M 1% /run/user/1000
In this example, the root directory “/” is located on the “/dev/sda3” partition which has a size of “55 GB.”
If the root partition is 8 GB or less, continue with this document.
If, however, the root partition is 20 GB or greater, please obtain Support Portal Knowledge Base Number 10048 – “Replacing the First Storage Drive using GParted on a Non-RAID exacqVision Ubuntu Linux Server having a 20 GB or larger ROOT partition.”
B. Temporarily Disabling the Original Drive Mount Point Listed in the fstab File
- Type the command sudo gedit /etc/fstab in Terminal and press the enter key to edit the file.
# /etc/fstab: static file system information.
#
# Use ‘blkid’ to print the universally unique identifier for a
# device; this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name devices
# that works even if disks are added and removed. See fstab(5).
#
# <file system> <mount point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
# / was on /dev/sda3 during installation
UUID=36a8d968-7e63-4859-a91b-0fdfcc319d3a / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1
# /boot/efi was on /dev/sda1 during installation
UUID=DDF2-8CC6 /boot/efi vfat umask=0077 0 1
# /home was on /dev/sda2 during installation
UUID=bc7b3ed7-7dfd-4530-972a-9c3269ea624b /home ext4 defaults 0 2
# /mnt/export was on /dev/sda4 during installation
UUID=e4638d65-fbe8-407c-a9e8-6c3da0bed19c /mnt/export ext4 defaults 0 2
/swapfile none swap sw 0 0
LABEL=/mnt/edvr/1 /mnt/edvr/1 ext4 relatime,errors=remount-ro,noauto,x-systemd.automount 0 0
2. Locate and add a “# ” remark character and a space to the beginning of the line for “/mnt/edvr/1”. Save the file.
# LABEL=/mnt/edvr/1 /mnt/edvr/1 ext4 relatime,errors=remount-ro,noauto,x-systemd.automount 0 0
3. Type the command sudo reboot in Terminal to restart the exacqVision Server.
C. Partitioning the First Non-RAID Storage Drive using GParted
- Open a Terminal session. Type the command sudo gparted and press the enter key. If prompted for a password, use the admin account password.
- Select the empty hard drive from the drop-down list in the top-right corner. Note that the drive is unallocated, which indicates that you have selected the correct hard drive. Select Create Partition Table from the Device menu.
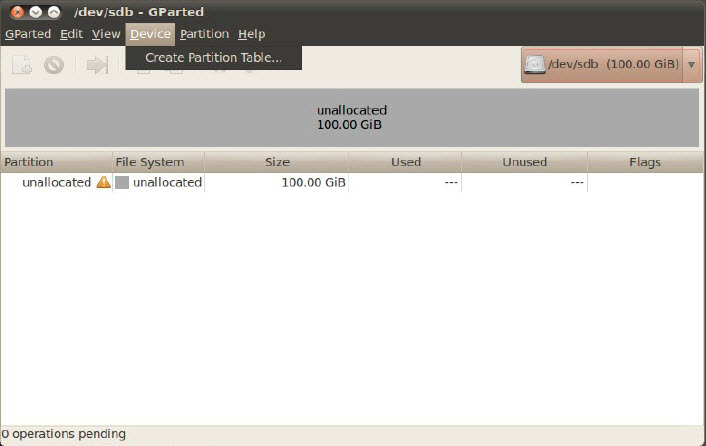
3. Select Advanced in the Create Partition Table dialog. Select gpt from the Select New Partition Table Type drop-down list. Click Apply.
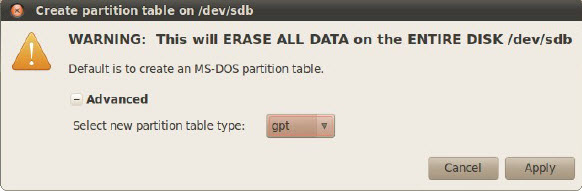
4. Right-click in the unallocated space and select New to open the Create New Partition window. Select 20000 in the New Size (MiB) box. Select linux-swap in the File System drop-down list. In the Label field, type swap. Click Add.
5. Right-click the unallocated space and select New to open the Create New Partition window. Select 10000 in the New Size (MiB) box. Select ext4 in the File System drop-down list. In the Label field, type /mnt/export. Click Add.
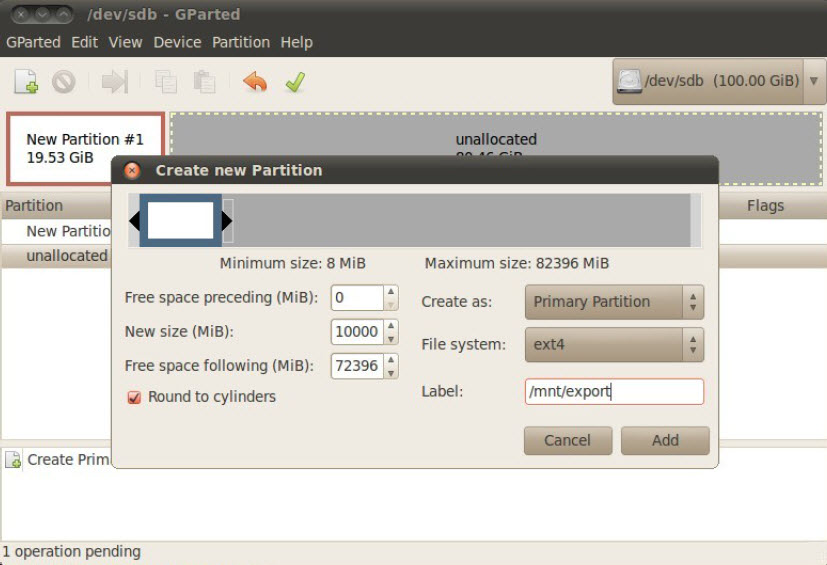
6. Right-click the unallocated space and select New to open the Create New Partition window. Select the highest available number in the Set New Size (MiB) box. Make sure Free Space Preceding and Free Space Following are both zero or 1. Select ext4 in the File System drop-down list. In the Label field, type /mnt/edvr/1. Click Add.
7. Click the green checkmark at the top of the screen and then click Apply. Wait for the operations to complete. Click on the Close button.
8. Close GParted.
9. In the terminal window, enter the following commands.
sudo service edvrserver stop
sudo mount –a
10. To create your export directories and change ownership:
sudo mkdir /mnt/export/admin
sudo mkdir /mnt/export/user
sudo chown admin /mnt/export/admin
sudo chown user /mnt/export/user
sudo service edvrserver start
11. In a Terminal window, enter the following commands:
sudo rm -r /home/admin/exacqVision\ Files
sudo rm -r /home/user/exacqVision\ Files
sudo ln -s /mnt/export/admin /home/admin/exacqVision\ Files
sudo ln -s /mnt/export/user /home/user/exacqVision\ Files
12. Run exacqVision Client and check the Storage configuration. You should see the new drive in the list of attached storage devices.
13. Type the command sudo gedit /etc/fstab in Terminal and press the enter key to edit the file.
# LABEL=/mnt/edvr/1 /mnt/edvr/1 ext4 relatime,errors=remount-ro,noauto,x-systemd.automount 0 0
- Locate and remove the “#” and space at the beginning of the line for “/mnt/edvr/1”. Save the file and closed the text editor.
LABEL=/mnt/edvr/1 /mnt/edvr/1 ext4 relatime,errors=remount-ro,noauto,x-systemd.automount 0 0
- Type the command sudo reboot in Terminal to restart the exacqVision Server. If prompted for a password, use the admin account password (admin256 by default).
D. The replaced drive may display as “Offline” in the Storage Page
- (A) If the old drive DOES NOT display as “Offline” in the Storage Page then the procedure is considered complete. (B) If the old drive DOES display as “Offline” then continue below.
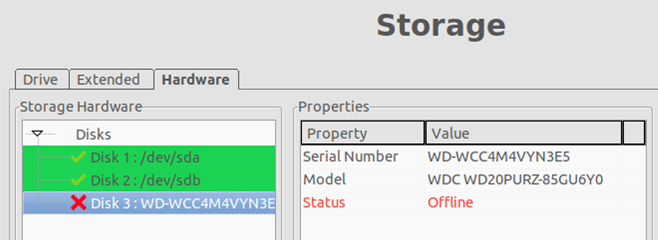
- Run exacqVision Client and check the Storage configuration. You should see the new drive in the list of attached storage devices. The replaced drive displays as “Offline” which requires editing the <sysmgmtpi.xml> file located in the path: /usr/local/exacq/server to remove the corresponding entries. Click on the “Offline” disk and note the model number and serial number for this purpose. Close the exacqVision Client.
- Open a Terminal session. Type the command sudo service edvrserver stop and press the enter key to stop the server service.
- Type the command cd /usr/local/exacq/server/ and press the enter key.
- Type the command sudo cp -via sysmgmtpi.xml sysmgmtpi.bak and press the enter key to back-up the original file.
- Type the command sudo gedit sysmgmtpi.xml and press the enter key. Scroll down and remove the lines (between and including the xml tags < Disk Name = > and < / Disk >) for the corresponding “Offline” hard disk drive model number and serial number noted previously with exacqVision Client. It should lack any < Attribute > tags.
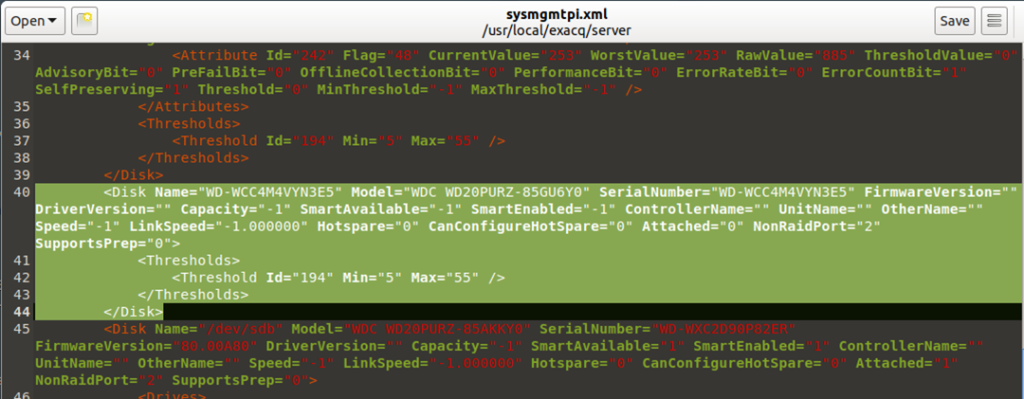
The section to be removed in our example:
< Disk Name = “WD-WCC4M4VYN3E5” Model=”WDC WD20PURZ-85GU6Y0″ SerialNumber=”WD-WCC4M4VYN3E5″ FirmwareVersion=”” DriverVersion=”” Capacity=”-1″ SmartAvailable=”-1″ SmartEnabled=”-1″ ControllerName=”” UnitName=”” OtherName=”” Speed=”-1″ LinkSpeed=”-1.000000″ Hotspare=”0″ CanConfigureHotSpare=”0″ Attached=”0″ NonRaidPort=”2″ SupportsPrep=”0″>
< Thresholds >
< Threshold Id = “194” Min=”5″ Max=”55″ />
< /Thresholds >
< /Disk >
- “Save” the changes and “Close” the gedit window.
- Type the command sudo service edvrserver start and press the enter key to start the server service.
- Close the Terminal window.
- Run exacqVision Client and check the Storage configuration is free of the “Offline” hard disk drive entry.
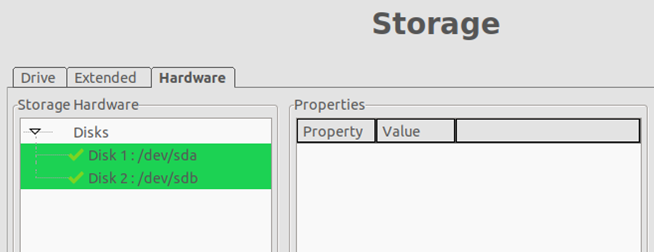
- Done.
<br>